The 2018 field season observations, conditions and summary. Field team Mariama Dryak, Erin McConnell, Jill Pelto and Mauri Pelto.
For the 35th consecutive year I headed to the North Cascade Range, Washington to monitor the response of glaciers to climate change. Two of the glaciers the North Cascade Glacier Climate Project (NCGCP) monitors are now part of the 42 glaciers comprising the World Glacier Monitoring Service (WGMS) reference glacier network, where annual mass balance has been assessed for more than 30 years consecutively.
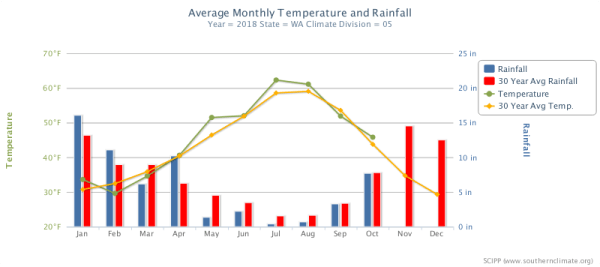
The 2018 winter season featured relatively normal snowpack despite a winter of wide temperature fluctuations, February freezing levels 400 m below the mean and December 500 m above the mean. Summer melt conditions featured temperatures 1.1 C above the 1984-2017 mean. The summer melt season through August was warm and exceptionally dry, which has also helped foster forest fires. The melt rate during the August field season was 35% above normal.
Washington Climate Division Five, western North Cascades
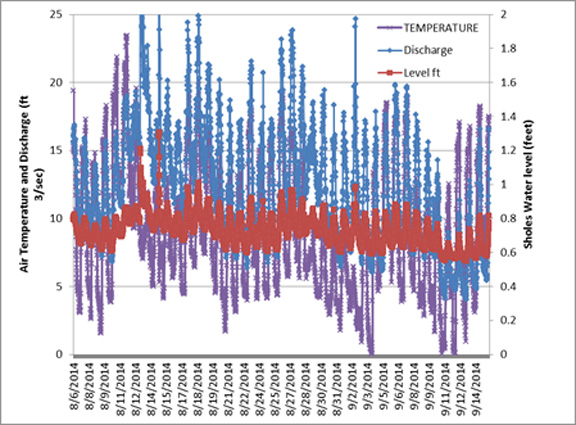
We assessed the mass balance of eight glaciers. All eight will have significant negative mass balances in 2018, between -0.5 m and -1.0 m. Retreat was measured on seven of the glaciers where the terminus was exposed, all had retreated since 2017 with the retreat ranging from 7-21 m. This continues the pattern of significant retreat each year that began in 2014. The overall length loss as a percentage of total length falls into a relatively narrow range of 10-22%. The mass balance losses has also led to additional rock outcrops emerging in what had been the elevation of the accumulation zone. We continued to measure runoff below Sholes Glacier and to assess crevasse depth. The average crevasse depth in 2018 was 10 m, with the deepest at 16 m on Lower Curtis Glacier.
Annual mass balance of North Cascade glaciers 1984-2018 (right). Cumulative glacier mass balance from NCGCP compared to WGMS global cumulative mass balance. Below is the retreat of selected North Cascade glaciers during the last 35 years, in meters and as a percentage of the total length. Locations for all but Columbia Glacier are in image below.
Mount Baker and Mount Shuskan glaciers identified in a Landsat image from 8-9-2018. Blue indicates mass balance and terminus change are observed. Orange indicates only terminus change is observed. C=Coleman, D=Deming, E=Easton, LC=Lower Curtis, M=Mazama, N=Nooksack, P=Price, R=Rainbow, Rv=Roosevelt, SH=Sholes.