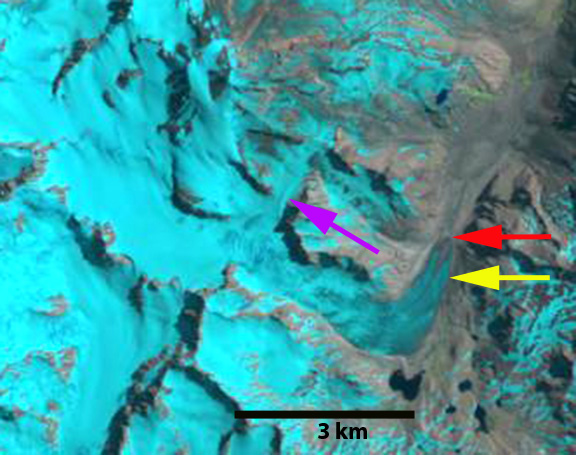
Cortaderal Glacier in Landsat images from 2014 and 2022. The glacier retreated 1400 m during this interval. The snowline in January 2014 is at 3750 m. On January 15, 2022 the snowline averages 4100 m with less than 15% snowcovered with 2.5 months left in the melt season. Red arrow is 2014 terminus and yellow arrow is 2022 terminus.
Cortaderal Glacier is a large valley glacier in Central Andes of Chile. Adjacent to the Universidad Glacier, it flows from Volcan Paloma (4860 m) and Nevado Penitente (4350 m) and drains into the Rio Cortaderal. Rio Cortaderal joins the Cachapoal River, that supplies two Pacific Hydro projects; a 110 MW run of river project at Chacayes and the 78 MW Coya run of river project a short distance downstream. The glacier is an important water resource from December-March. Bravo et al (2017) noted for Universidad Glacier that it supplied 10-13% of all runoff to the Tinguirica Basin during the melt season. La Quesne et al (2009) reported that Cortaderal Glacier retreated 110 m from 1970-2000 and 450 m from 2000-2007. Here we examine the retreat of this glacier from 2014-2022 and the unusually high snow lines in mid-January of 2022 due to the recent January heat wave (Washington Post, 2022).
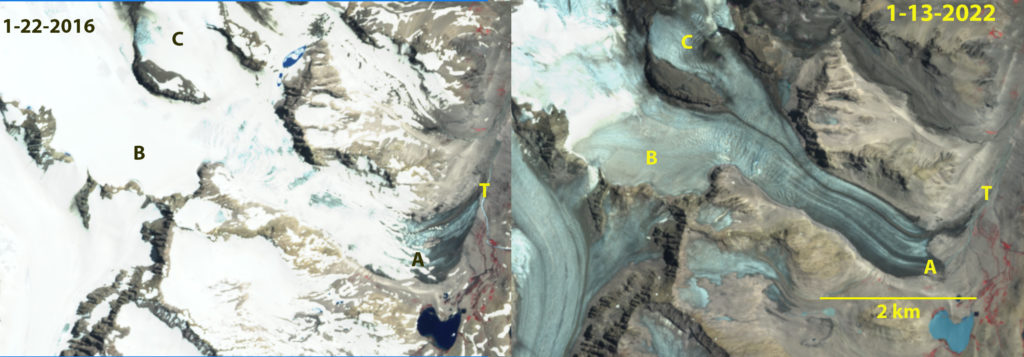
Cortaderal Glacier in Sentinel images from 2016 and 2022. Point A is the bedrock area that emerged in 2016 and was at the glacier front by 2022. Point T marks the 2016 terminus position, Point B is at 3750 m and Point C is at 4200 m. Snowline on January 22, 2016 is at 3200 m and averages 4100 m on January 13, 2022.
In February of 2014 the glacier terminated on the outwash plain at 2800 m. The snowline in mid January was at 3750 m. On January 9, 2016 the snowline was at 3200 m. At Point A a small bedrock area has emerged from beneath the ice 1 km upglacier of the terminus. On January 16, 2017 the snowline is at 3750 m. On January 19, 2019 the snowline is at 3700 m. The bedrock exposed at Point A is no longer surrounded by ice due to expansion and glacier retreat. On December 14th the snowline is at 3700 m and the glacier is 50% snowcovered. By January 15 there is less than 15 % snowcover, and the snowline averages 4100 m, nearly at the top of the glacier. With 10 weeks left in the melt season snowcover will decline further. This is reminiscent of reduced snowcover on glaciers in the Pacific Northwest due to the summer 2021 heat wave (Pelto, 2021).
The glacier has retreated to Point A, with an average frontal recession of 1300 m from 2014-2022. This is greater than the retreat from 1990-2014 of ~800-900 m (Pelto, 2014). The glacier now terminates at 3050 m in a region of much steeper slope that will reduce the retreat rate in the near future.
Cortaderal Glacier snow covered area change in two Landsat images one month apart. Snowcover declined from ~50% to 15%.
Cortaderal Glacier in Sentinel images from 2017 and 2019. Point A is the bedrock area that emerged in 2016 and was at the glacier front by 2022. Point T marks the 2016 terminus position, Point B is at 3750 m and Point C is at 4200 m. Snowline on January 16, 2017 is at 3750 m and averages 3700 m on January 19, 2019.
Landsat image indicating retreat from 1990-2014 of Cortaderal Glacier, red arrow 1990 position, yellow arrow 2014 position.



Pingback: Cortaderal Glacier, Chile 2022 Heat Wave Reduces Snow Cover, Retreat Continues - Traxense
Pingback: Losing a Layer of Protection - Inergency
Pingback: NASA: Lack of Snow Causing Rapid Glacier Melt in the Andes - SnowBrains